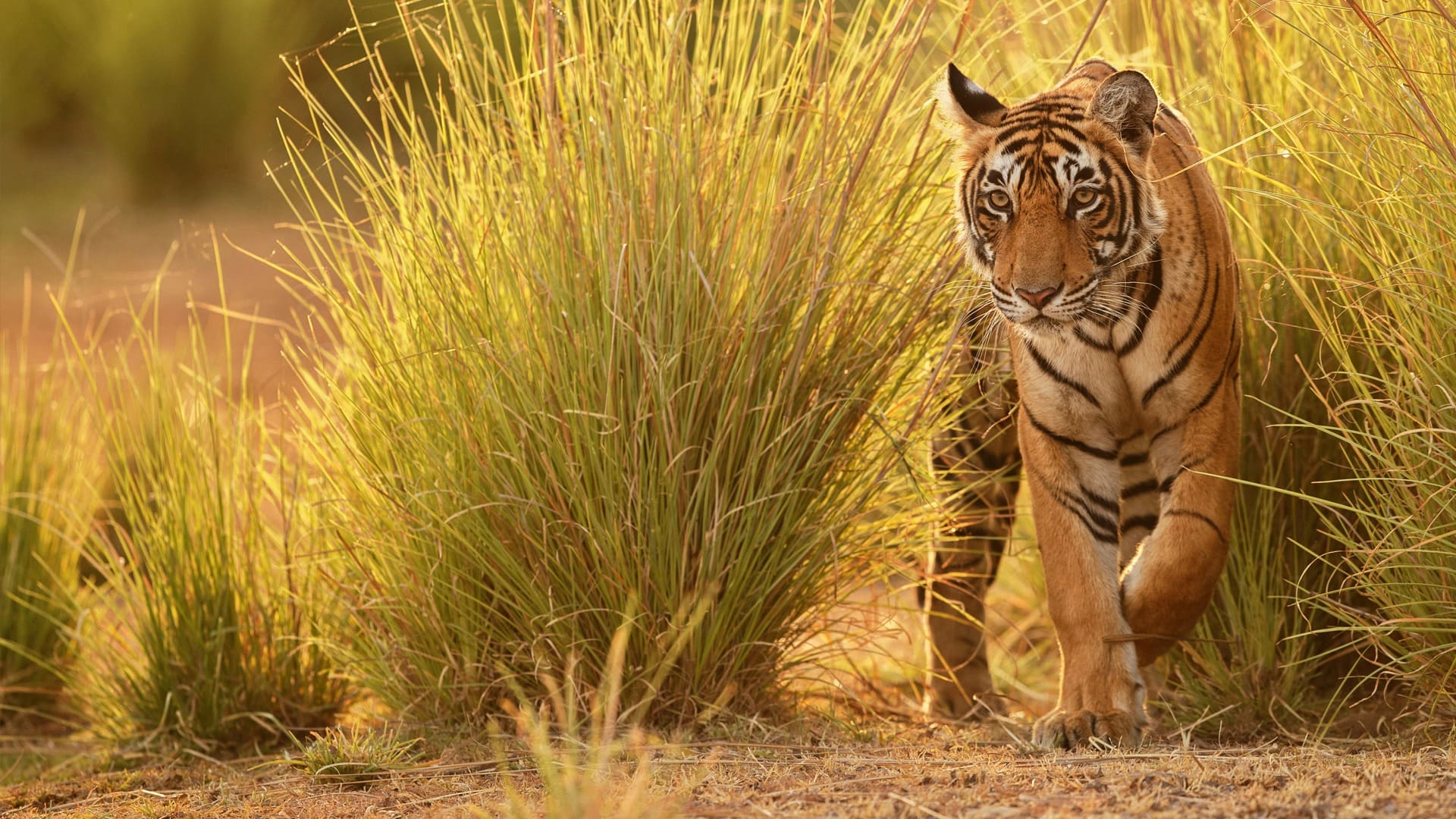

Story Of Pench

History of Pench
This area was described as extremely rich and diverse in wildlife from the earliest records available on the 16th century Deogarh kingdom (Ref: Kumar 1989). The scenic beauty and the floral and faunal diversity of the Central Indian Highlands have been well documented by the British since the late 17th century, e.g. Forsyth's (1919) [Ref: Highlands of Central India (first published in 1871)] Thereafter, Sterndale (1887) and Brander (1923) have added to the knowledge on the distribution of the flora, fauna and the local inhabitants of this tract.
The fictional works of Rudyard Kipling, The Jungle Book and The Second Jungle Book, are set in the region. Kipling himself never visited the area, instead basing his descriptions on other locations in India.
During the 17th century the Gond rulers of this region cleared large tracts of forests for cultivation and dwellings. This onslaught continued up to 1818, through the rule by the Marathas and later under the British. It was not until 1862 that efforts were made to control the indiscriminate destruction and the forests were declared reserved (Ref: Kumar 1989).

TIMELINE OF PENCH NATIONAL PARK
| S.No. | Year | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1977 | Declared Pench Sanctuary (449.392 sq km) |
| 2 | 1983 | Declared Pench National Park (292.857 sq km) 118.473 sq km remained as sanctuary and 38.062 excluded from umbrella of PA |
| 3 | 1992 | Included in Project Tiger |
| 4 | 1995 | Management of Sanctuary was handed over to Pench Tiger Reserve |
| 5 | 1998 | The Pench Sanctuary was finally notified by vide the Govt. of M.P. Forest Department's Notification no. F.15-65-96-X-2 Bhopal dated 21-8-1998. |
| 6 | 2002 | National Park was renamed as "Indira PriyadarshinigPench National Park" and Sanctuary was named as "Pench Mowgli Sanctuary" |
| 7 | 2005 | Final notification as "Indira PriyadarshiniPench National Park" vide notification dated 16.12.05 by MP Govt. no. F-15-11-05-x-02 |
| 8 | 2007 | Areas of National Park and Sanctuary are declared as Core of Pench Tiger Reserve Reserve notified dated 24.12.2007 by MP Govt. no. F-15-31-2007-X-2. |
| 9 | 2010 | The Buffer Zone of the tiger reserve has been notified F-15-8/2009/10-2 dated 05-10-2010 |
HOW PENCH GETS ITS NAME?
The Reserve gets its name from the Pench River that flows, north to south, 74 km through the reserve.It starts from Mahadeo hills of Satpura Ranges. The Pench River bisects the Pench Reserve into two nearly equal parts.It was declared a National Park in September 1977, with an initial area of 449.39 Sq. Km. On 1983 it was Declared Pench National Park and On 2005 The National Park is renamed as Indira Priyadarshini Pench National Park, carved out of the Sanctuary. The Tiger Reserve, 19th in the series, was formed under the Project Tiger scheme in November 1992. The area Core zone and Buffer zone were introduced in 2007 and 2010 respectively.

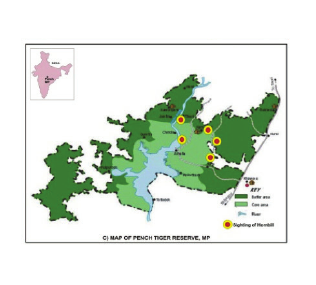
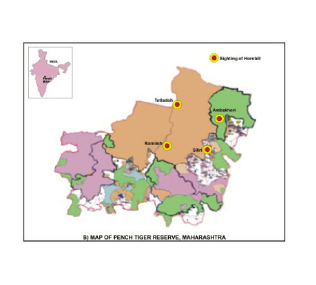
Madhya Pradesh Forest Area
| Core Area | 411.330 Sq. km. |
| Area of Indira PriyadarshiniPench National Park (Core) | 292.857 Sq. km. |
| Area of Pench Mowgli Sanctuary (Core) | 118.473 Sq. km. |
| Buffer area | 768.302 Sq. km. |
| Total Area of Pench Tiger Reserve (MP) | 1179.632 Sq. km |
Maharashtra Forest Area
| Core Area | 257.3 Sq. Km. |
| Buffer area | 483.96 Sq. Km |
| Total Area of Pench Tiger Reserve (MH) | 741.2 Sq. Km. |
